The FGFRs, are a family of four structurally-related receptor tyrosine kinases, namely FGFR1~4. These membrane-spanning receptors are activated in response to growth factor stimulation by dimerization, and result in trans-phosphorylation, which is followed by recruitment and phosphorylation of downstream intracellular substrates. FGFRs are precisely regulated in normal cells, but are constitutively activated in transformed cells involved in various human cancers, such as bladder cancer, pancreatic cancer, breast cancer, and prostate cancer. Aberrant activation of FGFRs has been observed in the process of tumorgenesis and tumor development. Thus, inhibition of FGFRs represents an attractive tumor therapeutic strategy.
8-oxo-8H-acenaphtho[1,2-b]pyrrol-carbonitrile (1) was previously discovered by QIAN Xuhong’s group from School of Pharmacy, East China University of Science and Technology and highlighted for its convenient synthesis and easy derivation. To date, compound 1 and its derivatives were functionalized for ion sensing, biomolecule imaging, tumor diagnosis. The antitumor capacity of acenaphtho[1,2-b]pyrrole derivatives was confirmed recently according to the antiproliferative assays with cancer cell lines including HeLa, MCF-7 and A549. However, other potential molecular targets of acenaphtho[1,2-b]pyrroles are not well explored. We report herein acenaphtho[1,2-b]pyrrole derivatives as a novel class of FGFR1 inhibitors with favorable SAR. Compared to other reported FGFR1 inhibitors, acenaphtho[1,2-b]pyrrole scaffold has been used for the first time as a tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
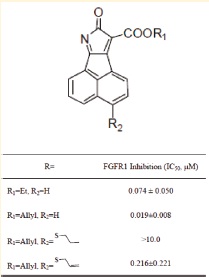
A. FGFR1 inhibition of some acenaphtho[1,2-b]pyrrole derivatives (Image by SIMM)

B. Predicted binding pose of representative acenaphtho[1,2-b]pyrrole derivative(Image by SIMM)
A novel series of acenaphtho[1,2-b]pyrrole derivatives as potent and selective inhibitors of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1) were designed and synthesized. In silico target prediction revealed that tyrosine kinases might be the potential targets of the representative compound 2, which was subsequently validated by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for its selective and active FGFR1 inhibition of various tyrosine kinases. The structure-activity relationship (SAR) analysis aided by molecular docking simulation in the ATP-binding site demonstrated that acenaphtho[1,2-b]- pyrrole-carboxylic acid esters (2-5) are potent inhibitors of FGFR1 with IC50 values ranging from 19 to 77 nM. Furthermore, these compounds exhibited favorable growth inhibition property against FGFR-expressing cancer cell lines with IC50 values ranging from micromolar to submicromolar. Western blotting analysis showed that compounds 2, 3 and 2b inhibited activation of FGFR1 and extracellular-signal regulated kinase 1/2 (Erk 1/2).
This research progress was collaboratively fulfilled by DING Jian research team from Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica(SIMM), Chinese Academy of Sciences and QIAN Xuhong and XU Yufang research team from School of Pharmacy, East China University of Science and Technology. The novel discovery was recently published on the latest issue of Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2011, 54:3732-3745.
Source:
Zhuo Chen, Xin Wang, Weiping Zhu, Xianwen Cao, Linjiang Tong, Honglin Li, Hua Xie*, Yufang Xu*, Shaoying Tan, Dong Kuang, Jian Ding, Xuhong Qian*. Acenaphtho[1,2-b]pyrrole-Based Selective Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptors 1 (FGFR1) Inhibitors : Design, Synthesis and Biological Activity. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2011, 54:3732-3745

