Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is a recently discovered human tumor virus, which has been identified as the etiological agent of three malignancies: Kaposi’s sarcoma (KS), primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) and multicentric Castleman disease (MCD). KSHV belongs to the gamma-2 herpesvirus subfamily. Following primary infection, the default pathway of KSHV infection is latency. However, the mechanism of which KSHV establishes latency is not fully understood.
To further understand the maintenance mechanism of viral latency, JIN Yi and her colleagues, supervised by Prof. LAN Ke at Institut Pasteur of Shanghai, Chinese Academy of Sciences, identified a motif in LANA C-terminal which is responsible for LANA interaction with RBP-Jκ. By reconstitution of the virus and analysis of the function of motif deficient LANA in the context of the full-length KSHV genome, they found that the interaction between LANA and RBP-Jκ was important for repressing viral lytic replication and maintaining KSHV latency. Their findings provide a valuable evidence for understanding the regulation of viral genes by a host transcription factor and its potential role in maintaining KSHV latency, It could be a potential target for disruption of viral latency, which could be a strategy for oncolytic viral therapy.
This work entitled “LANA Carboxyl Terminal Amino Acids 1052 to 1082 Interact with RBP-Jκ and are Responsible for LANA-Mediated RTA Repression" was published online in the Journal of Virology on February 29th, 2012.
This work was supported by grants from the ‘973’ Program, ’Hundred Talents Program’ of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and National Natural Science Foundation of China .
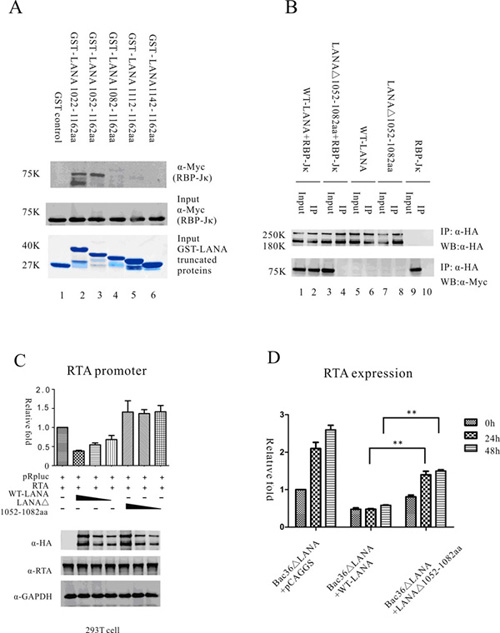
LANA C-ter 1052-1082aa Interact with RBP-Jκ (Image by JIN Yi etc.)

