Driven by increasing demand for high-energy-density batteries for consumer electronics and electric vehicles, substantial progress has been achieved in the development of long-life lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries. Less attention has been given to Li-S batteries with high volume energy density, which is crucial for applications in compact space. In a study published in Adv. Energy Mater, the research group led by Prof. WANG Ruihu from Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter (FJIRSM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) reported a series of elastic sandwich-structured cathode materials consisting of alternating VS2-attached reduced graphene oxide (rGO) sheets and active sulfur layers. Due to the high polarity and conductivity of VS2, a small amount of VS2 can suppress the shuttle effect of polysulfides and improve the redox kinetics of sulfur species in the whole sulfur layer. Sandwich-structured rGO-VS2/S composites exhibit significantly improved electrochemical performance, with high discharge capacities, low polarization and excellent cycling stability compared with their bare rGO/S counterparts. Impressively, the tap density of rGO-VS2/S with 89 wt% sulfur loading is 1.84 g cm-3, which is almost three times higher than that of rGO/S with the same sulfur content (0.63 g cm-3). The volumetric specific capacity of the whole cell is as high as 1182.1 mAh cm-3, comparable with the state-of-the-art reported for energy storage devices, demonstrating the potential for application of these composites in long-life and high-energy-density Li-S batteries. 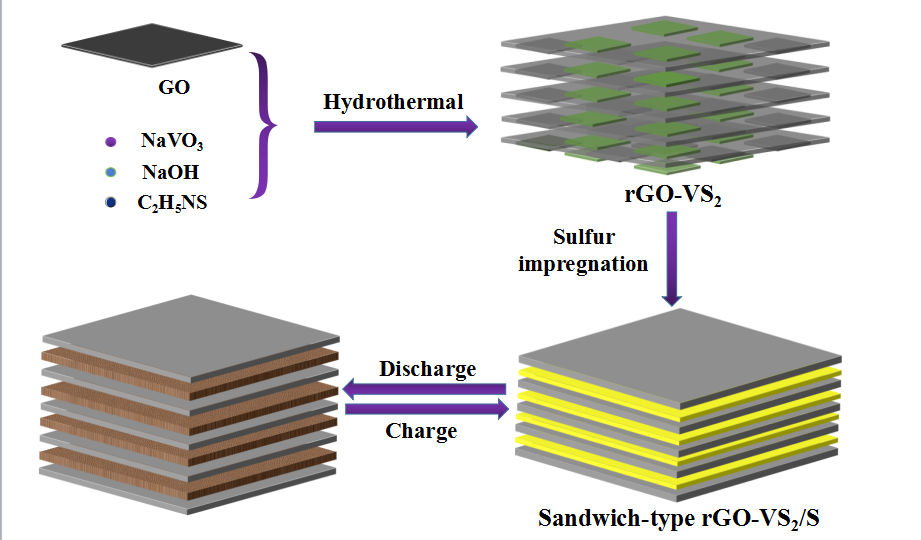
Schematic illustration for the synthesis of the sandwich-structured rGO-VS2/S composite.(Image by Prof. WANG’s Group) Contact: Prof. WANG Ruihu Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter Chinese Academy of Sciences Email: ruihu@fjirsm.ac.cn |

