Prof. WANG Zefeng’s group from Shanghai Institute of Nutrition and Health (SINH) of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) have recently reported a new programmable RNA base editing tool named REIWRE (RNA editing with individual RNA-binding enzyme) in Nucleic Acids Research on Aug. 27th, 2022, entitled “Programmable RNA base editing with a single gRNA-free enzyme”. This system contains a human-originated programmable PUF domain to specifically recognize RNAs, and different deaminase domains achieve efficient A-to-I or C-to-U editing. This system could achieve 60–80% editing rate in human cells, with a few non-specific editing sites in the targeted region and a low level off-target effect globally.
Base editing is a new genetic modification strategy that directly installs point mutations into the DNAs or RNAs without making pernicious breaks in nucleic acid chain. Compared to DNA manipulation, editing on RNAs is non-permanent and reversible, making it relative safer for in vivo application as a potential therapy. Previous reported RNA base editing tools dependent on the assembly of guide RNA into an RNA/protein complex, causing delivery barrier and low editing efficiency.
With different functional domains, the REWIREs can effectively achieve both A-to-I and C-to-U editing, and can be used in correcting pathogenic mutations of endogenous genes. The protein sequences of this system are entirely originated from human proteome, which could avoid the innate immunity from CRISPR-based system using bacterial proteins. Importantly, the REWIRE system achieved in vivo base editing in mice through systematic delivery with AAV, suggesting its potential in personalized gene therapy.
PhD students HAN Wenjian (now as Postdoc at Center for Excellence in Brain Science and Intelligence Technology of CAS) and HUANG Wendi are joint first authors, Dr. MAO Miaowei and Prof. WANG Zefeng are co-corresponding authors. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key Research and Development Program of China ,the Strategic Priority Research Program of CAS, the Starry Night Science Fund at Shanghai Institute for Advanced Study of Zhejiang University, Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality, the National Postdoctoral Program for Innovative Talents, Shanghai Super Postdoctoral Program, etc.
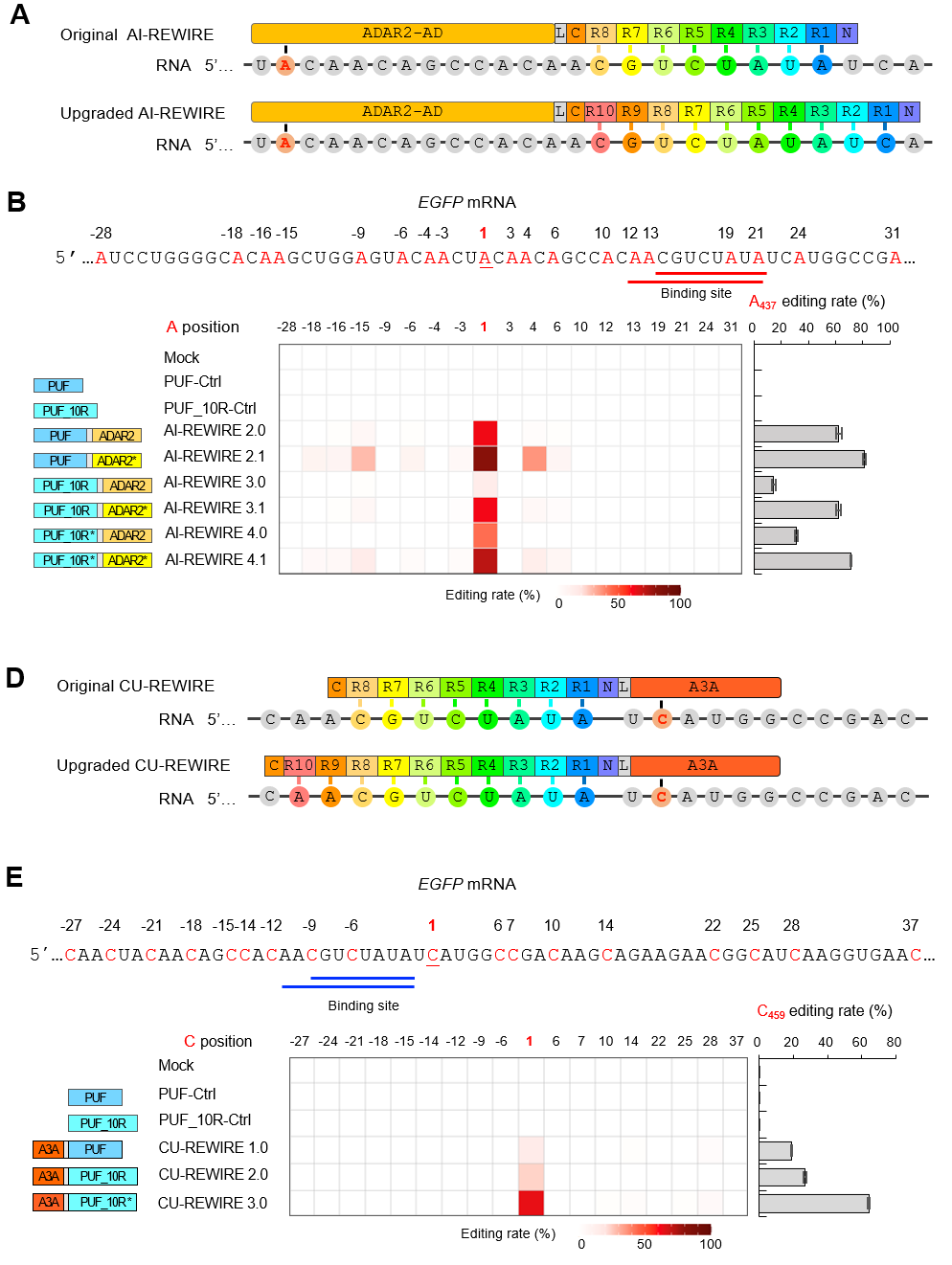
Schematic of REWIREs and the optimization strategies. (Image by Dr. WANG Zefeng's Group)
Media Contact:
WANG Jin (Ms.)
Shanghai Institute of Nutrition and Health,
Chinese Academy of Sciences
Email: wangjin01@sinh.ac.cn
Web: http://english.sinh.cas.cn/

